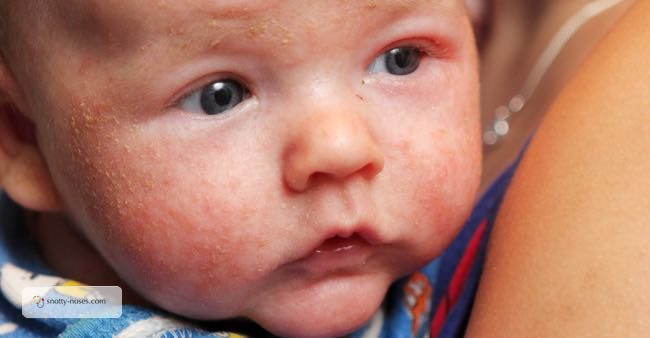
A child with severe eczema has red or discolored skin (usually under the neck, eczema on lips, under the arms, knees, and on the face) that is highly irritable and unyielding to generic over-the-counter lotions and creams. Eczema or atopic eczema is usually the skin’s way of reacting to something in the environment that the child is allergic to, or something that he/she is ingesting. For instance, some infants have allergies to milk, while others may be allergic to a certain detergent.
A trip to the pediatrician, lip lickers dermatitis or other eczema specialist is almost always necessary to gauge what prescription creams, natural eczema cream or drugs are needed to manage the child’s condition (as doctors say that eczema is not completely curable). Steroid creams may be prescribed or even oral steroids, if doctors feel the condition is too out-of-hand. According to Dr. Richard Antaya of Yale Dermatology Associates in New Haven, Ct, oral steroids have complicated side effects and should be avoided for children, if possible. He also suggests that if they are needed, they should be used only for a short period of time.
After nights of lost sleep and weeks to months of enduring an irritable child, parents may feel the situation hopeless and miserable — which may prompt a rush to consider oral steroid use. But before considering that method of treatment, please acquire more opinions from different doctors. And, ask them about the following successful eczema treatment practices.
Successful Eczema Treatments
Keep the child’s skin moisturized by:
Bathing twice a day for a week – Frequent baths soothe the skin and help add moisture. Bathtime is usually a fun time for any infant, but it’s especially exciting for those with eczema because they don’t feel itchy anymore and they get to play.
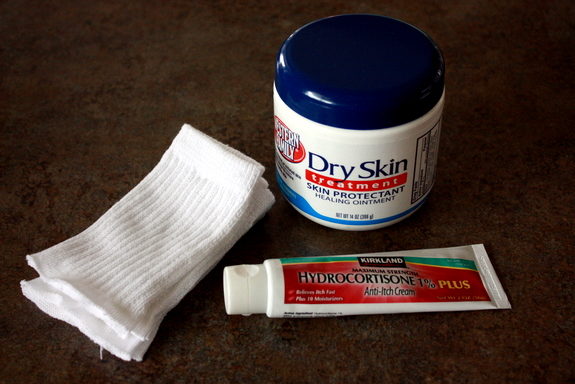
Stocking up on medical lotions like Eucerin – These so-called eczema lotions are designed specifically for such skin conditions, and they lock in skin moisture and keep prevent irritation. The key to eczema management is to prevent skin dryness. This lotion does that (and more).
In moisturizing, many parents find that Vaseline helps a lot. Others use Spectro Kids Intense Moisturizing Cream which is not sticky like Vaseline. For others, Cetaphil is the best for their baby. Experimenting is the key. Try different moisturizing products and find which one will work best for the baby. Just be sure that the product is fragrance-free because chemicals often trigger flare-ups.
Control Flare-ups of Eczema
When a baby has flare-ups, the skin tends to feel warm and this makes it very uncomfortable for the baby. It helps to pat the skin with cool towel (do not rub as this will harm the skin). Wet the towel with cold water and pat the skin with it.
If breastfeeding, watch out for foods that can trigger flare-ups. If the baby is given infant formula, try to switch to soy-based one. Detergent used in clothes should also be examined. See if a particular brand triggers flare-ups but to be sure, use hypoallergenic products for the baby’s clothes.
Using cortisone should be the last resort and should be used only as prescribed by the doctor. Cortisone makes the skin layer thin so be wary of using it. Some parents even find that using it makes their baby’s eczema worse. Apply only a very small amount to the affected areas and always consult the doctor if longer use is needed.
Seek specialized medical advice and assistance for the following:
Ask a pediatrician and a dermatologist about using a low-percent steroid cream like hydrocortisone valerate. This hydrocortisone is used to control severe eczema in infants and reduce skin inflammation. Every condition is unique, so your doctor will prescribe how many times the cream should be applied to your child’s skin, as well as how long it should be used.
Ask a pediatrician about anti-itching/anti-histamine medicine in the syrup/liquid form, not the cream), like Benadryl or Atarax: drugs used to treat allergic reactions by calming the histamine in the skin and making the child drowsy and less irritable
Eliminate environmental irritants and get familiar with the word hypo-allergenic:
If it can be a possible irritant, eliminate the child’s exposure. Possible irritants include: wool and polyester clothing and blankets, harsh detergents (try ALL clear or Dreft instead — both proven to be extra-gentle of baby skin), scented baby soaps — try Johnson & Johnson Head-to-Toe. It’s hypo-allergenic.)
Consider getting an air purifier. It gets rid of dust mites, allergens and the like.
Wash your clothes In ALL (Clear) or Dreft to prevent further irritation to child’s skin when handling
In order to manage infant eczema and have peace of mind, it may be necessary to make frequent trips to the eczema specialist to track the condition and improvement. Eczema is usually worse in the winter months, but with proper management and medical advice, parents do learn how to manage it. With treatment, eczema can calm down almost to non-existence. Just be persistent and patient.
Probiotics and Anti-Inflammatory Foods Reduce Itchiness and Redness
Probiotics from foods such as yogurt or supplements containing Lactobacillus rhamnosus bacteria, before and during pregnancy and by nursing mothers may help to decrease the risk of eczema in babies by up to 50 percent. Other foods that contain these healthy bacteria include miso, tempeh and kefir. Onions and bananas are a whole food source for probiotics.
Foods and supplements that decrease inflammation also help to decrease eczema symptoms. These include omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids that are found in fish, seafood, flax, and vegetable oils. Soothing allergen-free lotions that contain chamomile, calendula and burdock, help to decrease itching and inflammation.
Decrease Allergens At Home to Improve the Health of Children
It is important to prevent allergic reactions in infants and children that are susceptible to eczema. Perfumes and chemicals in soaps, lotions, shampoos and cleaning products that are directly used on children or transferred from a mother’s skin to an infant can trigger eczema flare-ups.
Allergenic foods such as milk, eggs, soy, nuts, peanuts, tomatoes, fish and wheat should be recorded in a food diary to determine if an infant has food allergies. A physician can diagnose a food allergy accurately. Dust, pollen and environmental allergens can also cause eczema. Reduce these in the home by vacuuming carpets and washing bedding and stuffed toys regularly.
- How to support your child’s mental health: A parent’s guide - February 1, 2025
- Can data centers stay green? Balancing digital growth with clean energy - January 26, 2025
- Why Blockchain could be end of high fees, delays in global payments - January 17, 2025
- Abridge AI: Silent scribe transforming healthcare interactions - January 5, 2025
- What makes quantum AI a game-changer for technology - December 25, 2024
- How businesses must adapt to evolving cyber threats in 2025 - December 4, 2024
- How vaping stiffens blood vessels and strains lungs: Study - November 26, 2024
- OpenAI Codex or Google Codey? Finding the perfect AI for your code - November 18, 2024
- What Google’s Project Jarvis means for future of digital interaction - October 28, 2024
- 11 tips for creating engaging ad content - July 8, 2024